Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Rizaal, M.; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Saito, Takumi*; Osaka, Masahiko; Okamoto, Koji*
ACS Omega (Internet), 7(33), p.29326 - 29336, 2022/08
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:27.64(Chemistry, Multidisciplinary)Rizaal, M.; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Saito, Takumi*; Osaka, Masahiko; Okamoto, Koji*
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 57(9), p.1062 - 1073, 2020/09
Times Cited Count:8 Percentile:70.65(Nuclear Science & Technology)The interaction of cesium hydroxide and a calcium silicate insulation material was experimentally investigated at high temperature conditions. A thermogravimetry equipped with differential thermal analysis was used to analyze thermal events in the samples of mixed calcium silicate and cesium hydroxide under Ar-5%H and Ar-4%H
and Ar-4%H -20%H
-20%H 0 with maximum temperature of 1100
0 with maximum temperature of 1100 C. Prior being mixed with cesium hydroxide, a part of calcium silicate was pretreated at high temperature to evaluate the effect of possible structural changes of this material due to a preceding thermal history and also the sake of thermodynamic evaluation to those available ones. Based upon the initial condition (preliminary heat treatment) of calcium silicate, it was found that if the original material consisted of xonotlite (Ca
C. Prior being mixed with cesium hydroxide, a part of calcium silicate was pretreated at high temperature to evaluate the effect of possible structural changes of this material due to a preceding thermal history and also the sake of thermodynamic evaluation to those available ones. Based upon the initial condition (preliminary heat treatment) of calcium silicate, it was found that if the original material consisted of xonotlite (Ca Si
Si 0
0 (0H)
(0H) ), the endothermic reaction with cesium hydroxide occurred over the temperature range 575-730
), the endothermic reaction with cesium hydroxide occurred over the temperature range 575-730 C meanwhile if the crystal phase of original material was changed to wollastonite (CaSi0
C meanwhile if the crystal phase of original material was changed to wollastonite (CaSi0 ), the interaction occurred over temperature range 700-1100
), the interaction occurred over temperature range 700-1100 C. Furthermore, the X-ray diffraction analyses have indicated on both type of pretreated calsils that regardless of Ar-5%H
C. Furthermore, the X-ray diffraction analyses have indicated on both type of pretreated calsils that regardless of Ar-5%H and Ar-4%H
and Ar-4%H -20%H
-20%H 0 atmosphere, cesium aluminum silicate, CsAlSi0
0 atmosphere, cesium aluminum silicate, CsAlSi0 was formed with aluminum in the samples as an impurity or adduct.
was formed with aluminum in the samples as an impurity or adduct.
Nakajima, Kunihisa; Nishioka, Shunichiro*; Suzuki, Eriko; Osaka, Masahiko
Mechanical Engineering Journal (Internet), 7(3), p.19-00564_1 - 19-00564_14, 2020/06
A large amount of cesium (Cs) chemisorbed onto stainless steel is predicted to be present especially in the upper region of reactor pressure vessel (RPV) during light water reactor severe accident (LWR SA) and a chemisorption model was developed for estimation of such amounts of Cs for stainless steel type 304 (SS304). However, this existing chemisorption model cannot accurately reproduce experimental results. Therefore, in this study, a modified Cs chemisorption model which accounts for silicon content in SS304 and concentration of cesium hydroxide (CsOH) in gaseous phases was constructed by combining penetration theory for gas-liquid mass transfer with chemical reaction and mass action law for CsOH decomposition at interface between gaseous and solid phases. As a result, it was found that the modified model was able to reproduce the experimental data more accurately than the existing model.
Nishioka, Shunichiro; Nakajima, Kunihisa; Suzuki, Eriko; Osaka, Masahiko
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 56(11), p.988 - 995, 2019/11
Times Cited Count:12 Percentile:79.53(Nuclear Science & Technology)In order to contribute to improvement of Cs chemisorption model used in severe accident analysis codes, the influence of chemical factors (temperature, atmosphere, concentration of affecting chemical elements etc.) on the Cs chemisorption behaviour onto stainless steel was investigated experimentally. It was found that the surface reaction rate constant used in the current Cs-chemisorption model was influenced by not only temperature, as already known, but also atmosphere, cesium hydroxide (CsOH) concentration in the gas phase and silicon content in SS304. Such chemical factors should be considered for the construction of the improved Cs-chemisorption model. Another important finding is that the chemisorption behavior at lower temperatures, around 873 K, could differ from those above 1073 K. Namely, Cs-Fe-O compounds would form as the main Cs-chemisorbed compounds at 873 K while Cs-Si-Fe-O compounds at more than 1073 K.
Kobayashi, Taishi*; Teshima, Takeshi*; Sasaki, Takayuki*; Kitamura, Akira
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 54(2), p.233 - 241, 2017/02
Times Cited Count:6 Percentile:50.9(Nuclear Science & Technology)Zr solubility in the presence of gluconic acid (GLU) and isosaccharinic acid (ISA) was investigated as a function of hydrogen ion concentration (pH ) and the total concentration of GLU or ISA. The dependence of the increase in Zr solubility on the pH
) and the total concentration of GLU or ISA. The dependence of the increase in Zr solubility on the pH and GLU concentration suggested the existence of Zr(OH)
and GLU concentration suggested the existence of Zr(OH) (GLU)
(GLU)
 in the neutral pH region and Zr(OH)
in the neutral pH region and Zr(OH) (GLU)(GLU
(GLU)(GLU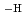 )
) in the alkaline pH region above pH
in the alkaline pH region above pH 10 as the dominant species in the presence of 10
10 as the dominant species in the presence of 10 - 10
- 10 mol/dm
mol/dm (M) GLU. In the presence of ISA, the dominant species Zr(OH)
(M) GLU. In the presence of ISA, the dominant species Zr(OH) (ISA)
(ISA)
 and Zr(OH)
and Zr(OH) (ISA)(ISA
(ISA)(ISA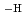 )
) were proposed to occur in the neutral and alkaline pH regions, similar to those found in the presence of GLU. From X-ray diffraction analysis, the solubility-limiting solid phase in the presence of GLU and ISA was considered to be Zr(OH)
were proposed to occur in the neutral and alkaline pH regions, similar to those found in the presence of GLU. From X-ray diffraction analysis, the solubility-limiting solid phase in the presence of GLU and ISA was considered to be Zr(OH) (am). The formation constants of the Zr gluconate and isosaccharinate complexes were determined by least squares fitting analysis of the solubility data, and the obtained values were discussed in comparison with those of tetravalent actinides.
(am). The formation constants of the Zr gluconate and isosaccharinate complexes were determined by least squares fitting analysis of the solubility data, and the obtained values were discussed in comparison with those of tetravalent actinides.
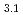 (OCOCH
(OCOCH )
)
 0.9H
0.9H O
OKozai, Naofumi; Mitamura, Hisayoshi; Fukuyama, Hiroyasu; Esaka, Fumitaka; Komarneni, S.*
Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 89(1-3), p.123 - 131, 2006/03
Times Cited Count:11 Percentile:39.24(Chemistry, Applied)Layered transition metal hydroxide salt (LTMHS) is a group of anion-exchangeable layered compounds. Although LTMHSs have recentely attracted attention of researches on anion exchange and intercalation, very limited numbers of reports have been published on their synthesis, characteristics, and applications. This paper describes basic characteristics of a new LTMHS, nickel-copper hydroxide acetate. Hydrothermal Heating of an aqueous solution containing nickel acetate, copper acetate, and hydrogen peroxide to 150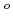 C for 4h yielded a layered compound with an analytical composition of NiCu(OH)
C for 4h yielded a layered compound with an analytical composition of NiCu(OH)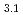 (OCOCH
(OCOCH )
) 0.9H
0.9H O. This compound does not take up Cl
O. This compound does not take up Cl and NO
and NO
 in aqueous solution but takes up multivalent anions and shows high selectivity in uptake of toxic SeO
in aqueous solution but takes up multivalent anions and shows high selectivity in uptake of toxic SeO
 and AsO
and AsO
 . This compound may find applicarion in the removal of those toxic anions form natural water and wastewater rich in Cl
. This compound may find applicarion in the removal of those toxic anions form natural water and wastewater rich in Cl and NO
and NO
 .
.
Kozai, Naofumi; Mitamura, Hisayoshi; Fukuyama, Hiroyasu; Esaka, Fumitaka; Komarneni, S.*
Journal of Materials Research, 20(11), p.2997 - 3003, 2005/11
Layered transition metal hydroxide salt (LTMHS) is a group of anion-exchangeable layered compounds. LTMHSs have lately attraced attention of researchs on anion exchange and intercalation but very limited numbers of reports have been published on their synthesis, characteristics, and application. This study reports basic properties of a layered copper hyroxide acetate synthesized by a method modified from that of the previous studies. Titration of copper acetate solution with a dilute NaOH solution to pH 6.5 and subsequent aging at 313 K yielded a layered copper hydroxide acetate. This compound has some properties similar to those of the previously known copper hydroxide acetate, Cu (OH)
(OH) (OCOCH
(OCOCH )H
)H O. The present copper hydroxide acetate is dissimilar to the previous compound in morphology, stability of bonding between the interlayer acetate ions and the matrix hydroxides, and reaction with anions in aqueous solutions.
O. The present copper hydroxide acetate is dissimilar to the previous compound in morphology, stability of bonding between the interlayer acetate ions and the matrix hydroxides, and reaction with anions in aqueous solutions.
Nagase, Kenzo*; Morita, Noboru*; Watanabe, Akiyoshi*; Asao, Toyonobu*
JAERI-Tech 2005-052, 99 Pages, 2005/09
no abstracts in English
Nakayama, Shinichi; Sakamoto, Yoshifumi; Yamaguchi, Tetsuji; Akai, Masanobu; Tanaka, Tadao; Sato, Tsutomu*; Iida, Yoshihisa
Applied Clay Science, 27(1-2), p.53 - 65, 2004/10
Times Cited Count:83 Percentile:89.21(Chemistry, Physical)Alkaline environments induced by cement in radioactive waste repositories are likely to alter montmorillonite, the main constituent of bentonite buffer materials. Over long time periods, the alteration may cause the physical and/or chemical properties of the buffer to deteriorate. For the purpose of acquiring numerical data to quantify the effect of alteration on permeability of bentonite buffer, dissolution rates of montmorillonite and diffusivity of hydroxide ions in compacted sand-bentonite mixture specimens have been measured under highly alkaline, simulated groundwater conditions. The dissolution rate of montmorillonite was given by the linear dependence on time under the employed experimental conditions of pH 13 to 14 and temperatures of 90 to 170 C. The diffusivity of hydroxide ions was obtained in through-diffusion experiments combined with a pore diffusion model. The experiments were performed under relatively low temperatures of 10 to 50
C. The diffusivity of hydroxide ions was obtained in through-diffusion experiments combined with a pore diffusion model. The experiments were performed under relatively low temperatures of 10 to 50 C to minimize the effect of alteration of bentonite. The effective diffusivity was on the order of 10
C to minimize the effect of alteration of bentonite. The effective diffusivity was on the order of 10 to 10
to 10 m
m /s.
/s.
Fujie, Makoto; *; *; *
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 23(4), p.330 - 337, 1986/00
Times Cited Count:46 Percentile:96.4(Nuclear Science & Technology)no abstracts in English
Furukawa, Kazuo; *
Boshoku Gijutsu, 29(4), p.185 - 195, 1980/00
no abstracts in English